Packages This Package Prev Next Index
§1.16 Class FlowLayout
public class java.awt.FlowLayout
extends java.lang.Object (I-§1.12)
implements java.awt.LayoutManager (II-§1.43)
{
// Fields
public final static int CENTER; §1.16.1
public final static int LEFT; §1.16.2
public final static int RIGHT; §1.16.3
// Constructors
public FlowLayout(); §1.16.4
public FlowLayout(int align); §1.16.5
public FlowLayout(int align, int hgap, int vgap); §1.16.6
// Methods
public void addLayoutComponent(String name, §1.16.7
Component comp);
public void layoutContainer(Container target); §1.16.8
public Dimension minimumLayoutSize(Container target); §1.16.9
public Dimension preferredLayoutSize(Container target); §1.16.10
public void removeLayoutComponent(Component comp); §1.16.11
public String toString(); §1.16.12
}
A Flow layout arranges components in a left-to-right flow, much like lines of text in a
paragraph. Flow layouts are typically used to arrange buttons in a panel.
For example, the following picture shows an Applet using the flow layout manager (its
default layout manager) to position three buttons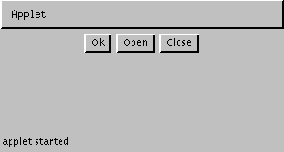 :
:
Here is the applet code:
import java.awt.*;
import java.applet.Applet;
public class myButtons extends Applet {
Button button1, button2, button3;
public void init() {
button1 = new Button("Ok");
button2 = new Button("Open");
button3 = new Button("Close");
add(button1);
add(button2);
add(button3);
}
}
A flow layout lets each component take its natural (preferred) size.
CENTER
public final static int CENTER = 1
- This value indicates that each row of components should be centered.
LEFT
public final static int LEFT = 0
- This value indicates that each row of components should be left justified.
RIGHT
public final static int RIGHT = 2
- This value indicates that each row of components should be right justified.
FlowLayout
public FlowLayout()
- Creates a new flow layout manager with a centered alignment and a
default 5-pixel horizontal and vertical gap.
FlowLayout
public FlowLayout(int align)
- Creates a new flow layout manager with the indicated alignment and a
default 5-pixel horizontal and vertical gap.
- The alignment argument must be one of FlowLayout.LEFT, FlowLayout.RIGHT, or FlowLayout.CENTER.
- Parameters:
align
- the alignment value
FlowLayout
public FlowLayout(int align, int hgap, int vgap)
- Creates a new flow layout manager with the indicated alignment and the
indicated horizontal and vertical gaps.
- The alignment argument must be one of FlowLayout.LEFT, FlowLayout.RIGHT, or FlowLayout.CENTER.
- Parameters:
align
- the alignment value
hgap
- the horizontal gap between components
vgap
- the vertical gap between components
addLayoutComponent
public void addLayoutComponent(String name, Component comp)
- This method is not used by the flow layout manager.
- Parameters:
name
- a tag
comp
- the component to be added
layoutContainer
public void layoutContainer(Container target)
- Lays out the container argument using this layout.
- This method lets each component take its preferred size.
- Most applications do not call this method directly. This method is called
when a container calls its layout method (II-§1.11.11).
- Parameters:
target
- the container in which to do the layout
- See Also:
- Container (II-§1.11).
minimumLayoutSize
public Dimension minimumLayoutSize(Container target)
- Determines the minimum size of the target container using this flow layout.
- The minimum width needed to lay out the container's components is the
total minimum width of each of the components, plus (ncomponents + 1)
times the horizontal gap, plus the left and right inset, where ncomponents is
the number of components in the container.
- The minimum height needed to lay out the container's components is the
greatest minimum height of the components, plus twice the vertical gap,
plus the top and bottom insets.
- Most applications do not call this method directly. This method is called
when a container calls its layout method (II-§1.11.11).
- Parameters:
target
- the container in which to do the layout
- Returns:
- the minimum dimensions needed to lay out the subcomponents of the
specified container.
- See Also:
- preferredLayoutSize (II-§1.16.10).
preferredLayoutSize
public Dimension preferredLayoutSize(Container target)
- Determines the preferred size of the target container using this flow layout.
- The preferred width to lay out the container's components is the total preferred width of each of the components, plus (ncomponents + 1) times the
horizontal gap, plus the left and right inset, where ncomponents is the number of components in the container.
- The preferred height to lay out the container's components is the greatest
preferred height of the components, plus twice the vertical gap, plus the
top and bottom insets.
- Most applications do not call this method directly. This method is called
when a container calls its preferredSize method (II-§1.11.17).
- Parameters:
parent
- the container in which to do the layout
- Returns:
- the preferred dimensions to lay out the subcomponents of the specified container.
- See Also:
- Container (II-§1.11)
minimumLayoutSize (II-§1.16.9).
removeLayoutComponent
public void removeLayoutComponent(Component comp)
- Removes the specified component from this layout.
- Most applications do not call this method directly. This method is called
when a container calls its remove (II-§1.11.19) or removeAll (II-§1.11.20)
methods.
- Parameters:
comp
- the component to be removed
toString
public String toString()
- Returns:
- a string representation of this layout.
- Overrides:
- toString in class Object (I-§1.12.9).
Packages This Package Prev Next Index
Java API Document (HTML generated by dkramer on April 22, 1996)
Copyright © 1996 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
All rights reserved
Please send any comments or corrections to doug.kramer@sun.com
 :
: